Installing Agent Based OpenShift 4.14 on VMware vSphere
Table of contents
Agent Based OpenShift 4.14 on VMware vSphere
Cisco ACI supports Agent Based Red Hat OpenShift 4.14 on VMware vSphere. This document provides the instructions to provision OpenShift 4.14 on VMware vSphere with the Container Network Interface (CNI) plug-in.
Prerequisites for Installing Agent Based OpenShift 4.14 on VMware vSphere
To install Agent Based OpenShift Container Platform (OCP) 4.14 on VMware vSphere, fulfill the following prerequisites:
Cisco ACI
- Download the acc-provision tool version
6.0.4.1or later. - Specify the
--flavoroption value asopenshift-4.14-agent-based-esxand use the-zoption. - The tool creates a
.tararchive file as specified by the-zoption value. You need this archive file during installation. Make sure that the Cisco ACI container images that are specified as input to the acc-provision tool are version6.0.4.1or later.
VMware vSphere
Obtain user credentials with privileges to create virtual machines (VMs).
OpenShift
Obtain the following from the Red Hat website:
OCP4 client tools- navigate to the mirror page on the OpenShift website where the installation and client tool versions are listed, and select the required version.- Download the
openshift-client-linux.tar.gzandopenshift-install-linux.tar.gzfiles. - Pull Secret
Installing Agent Based OpenShift 4.14 on VMware vSphere
Before you begin
Complete the tasks in the previous section: Prerequisites for Installing Agent Based OpenShift 4.14 on VMware vSphere . It is recommended to see the RedHat OpenShift documentation for prerequisites and other details about Installing a Cluster on vSphere
Configuring ACI Infra and CNI
Use this procedure for configuring ACI infra and CNI using acc-provision.
Procedure
Procedure
Step 1.
- Provision the Cisco ACI fabric using the acc-provision utility:
- Customize the sample acc-provision input file as per your requirements. Then, install the latest acc-provision package from https://pypi.org/project/acc-provision/ and run pip install acc-provision .
- Run the acc-provision as follows:
$ ~/openupi$ pwd /home/<user>/openupi $ ~/openupi$ acc-provision -a -c acc_provision_input.yaml -f openshift-4.14-agent-based-esx -u <user> -p <password> -o aci_deployment.yaml -z aci deployment.yaml.tar.gz
This generates a new aci_deployment.yaml.tar.gz file which contains the ACI CNI manifests, and is used later during the OpenShift installation.
Note See acc-provision-input file in Sample Files section.
Note acc-provision tool is supported to run on RHEL8 and RHEL9 operating system.
Step 2.
- After the Cisco ACI fabric is provisioned, verify that a port group with the name system_id_vlan_kubeapi_vlan is created under distributed switch.
- This document refers to this port group as api-vlan-portgroup.
Note api-vlan-progroup port-group in VMware Distributed Virtual Switch is created using custom VLAN ID provided in the acc_provision_input file as kubeapi_vlan.
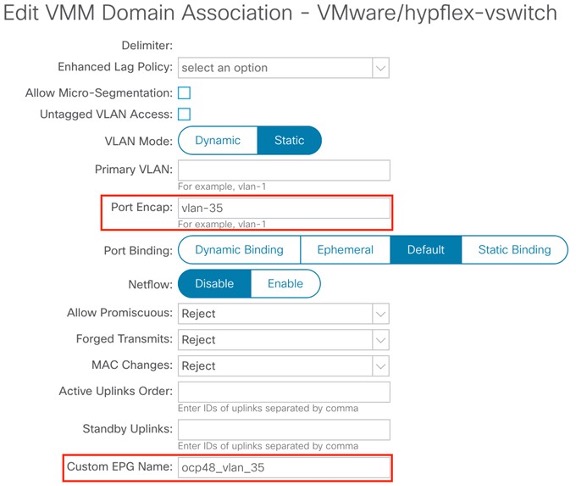
Figure 1: VMM VMware domain association with aci-containers-nodeEPG
Kube_api VLAN is added to the dynamic VLAN pool associated with the Vmware VMM Domain. Allocation mode will be set to Static

Figure 2: VLAN Pool used for VMM Vmware domain
Preparing Custom Network Configuration for OpenShift Nodes
ACI CNI requires additional VLANs to be extended towards each OpenShift node. Additional VLANS are required for master and worker nodes, but not required for the bootstrap node.
You can configure additional VLANs on the interface that will be configured with the node network subnet, or can be configured on an additional physical interface on the hosts.
The available option to configure network interface of a host is to provide the configuration in agent-config.yaml in NMState format. See Sample agent-config File Section
Agent-Config File Modification
Before you begin
The agent-config file, with additional NIC configuration, required to extend the Cisco ACI internal network (Infra VLAN) up to the server level. This interface is used to carry VxLAN traffic from OVS towards the ACI leaf switch with an appropriate tag for the pod network. The configuration offers below option for node and pod network configuration:
- Single Sub interface for both node and infra networks.
The option illustrated as shown below:
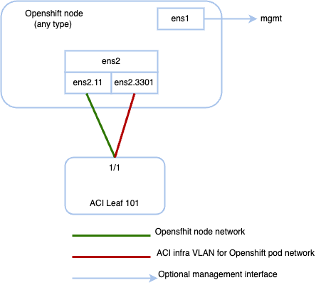
Note Node network is configured as VLAN subinterface of either bond0 or Virtual machine NIC. You can configure the server with additional VLAN(s) for management purpose or use the node network for management network. The design might be dependent on the server provisioning method (PXE or manual ISO boot).
apiVersion: v1alpha1
kind: AgentConfig
metadata:
name: ocpvmw11
rendezvousIP: 192.168.12.3 -> A
AdditionalNTPSources:
- time.cisco.com
hosts: -> B
- hostname: ocpvmw11-master1 -> C
role: master
interfaces:
- name: ens192
macAddress: 00:50:56:97:2a:d6
networkConfig: -> D
interfaces:
- name: ens192
mtu: 9000
ipv4:
enabled: false
ipv6:
enabled: false
- name: node
type: vlan
mtu: 9000
state: up
vlan:
base-iface: ens192
id: 131
ipv4:
enabled: true
address:
- ip: 192.168.12.3
prefix-length: 24
dhcp: false
ipv6:
enabled: false
- name: infra
type: vlan
mtu: 9000
state: up
vlan:
base-iface: ens192
id: 3301
ipv4:
enabled: true
dhcp: true
ipv6:
enabled: false
dns-resolver:
config:
server:
- 192.168.12.2
routes:
config:
- destination: 0.0.0.0/0
next-hop-address: 192.168.12.1
next-hop-interface: node
- destination: 224.0.0.0/4
next-hop-interface: infra
A. This IP address is used to determine which node performs the bootstrapping process as well as running the assisted-service component. You must provide the rendezvous IP address when you do not specify at least one host’s IP address in the networkConfig parameter. If this address is not provided, one IP address is selected from the provided hosts’ networkConfig
B. Host configuration. The number of hosts defined must not exceed the total number of hosts defined in the install-config.yaml file, which is the sum of the values of the compute.replicas and controlPlane.replicas parameters
C. Overrides the hostname obtained from either the Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) or a reverse DNS lookup. Each host must have a unique hostname supplied by one of these methods
D. Configures the network interface of a host in NMState format.
Procedure
Step 1 Create a root folder for your cluster.
cd /home/<user>/openupi mkdir upi
Step 2 Copy the install-config.yaml, agent-config.yaml in the newly created upi folder. Refer install-config and agent-config in Sample Files Section
Step 3 Create the openshift directory
mkdir -p /home/<user>/openupi/upi/opensfhit
Step 4 Extract all the ACI manifest files in upi/openshift/.
tar -xvf aci_deployment.yaml.tar.gz -C upi/openshift/
Step 5 Create the iso image.
openshift-install agent create image –dir=upi –log-level debug
Step 6 Boot the agent.x86_64.iso image on the virtual machines
The agent.x86_64.iso is now ready and can be uploaded to associated datastore or manually copied to the host volumes so they can be served to your nodes. The agent.x86_64.iso file will be consumed by every node and the network configuration for each node will be recognized based on the mac-address mention in NMState configuration for each node.
Step 7 Create the VMs – Refer Sample agent-config file for naming reference.
-
Provide name of the host (master/worker) as mentioned in agent-config.yaml hostname field
-
Select system_id_vlan_kubeapi_vlan as the network. Edit the mac address to match with the mac address mentioned for the VM in the agent-config.yaml.
-
Enable disk UUID – Click VM Options tab, and select Advanced. Click Edit Configuration in Configuration Parameters. Click Add parameter. In the Key column, type disk.EnableUUID. In the Value column, type TRUE. Click OK and click Save.
-
Select the uploaded image agent.x86_64.iso in the associated datastore
What to do next
You can use the commands openshift-install agent wait-for
bootstrap-complete and openshift-install agent wait-for install-complete
to check the progress of the installation. Execute the commands from the
bootstrap directory.
Sample Files
This section contains sample files that you need for installing agent based OpenShift 4.14 on Vmware vSphere.
Sample acc-provision-input File
The following is a sample acc-provision-input.yaml. The highlighted or bold values are those that you must modify to meet your site requirements.
aci_config:
system_id: ocp4aci
#apic-refreshtime: 1200
apic_hosts:
- 1.1.1.1
vmm_domain:
encap_type: vxlan
mcast_range:
start: 225.28.1.1
end: 225.28.255.255
nested_inside:
type: vmware
name: my-vswitch
elag_name: <eLAG_name>
# The following resources must already exist on the APIC.
# They are used, but not created, by the provisioning tool.
Aep: my-aep
vrf: # This VRF used to create all kubernetes Eps
name: myl3out_vrf
tenant: common
l3out:
name: myl3out
external_networks:
- myl3out_net
agent_based_installer:
enable: true
#
# Networks used by ACI containers
#
net_config:
node_subnet: 192.168.18.1/24
pod_subnet: 10.128.0.1/16
extern_dynamic: 10.3.0.1/24
extern_static: 10.4.0.1/24
node_svc_subnet: 10.5.0.1/24 # Subnet to use for service graph
kubeapi_vlan: 131
service_vlan: 132
infra_vlan: 3301
#interface_mtu: 1600
#service_monitor_interval: 5 # IPSLA interval probe time for PBR tracking
# default is 0, set to > 0 to enable, max: 65535
#pbr_tracking_non_snat: true # Default is false, set to true for IPSLA to
# Subnet to use for Kubernetes
# Pods/CloudFoundry containers
# Subnet to use for dynamic external IPs
# Subnet to use for static external IPs
# be effective with non-snat services
# Configuration for container registry
# Update if a custom container registry has been setup
#
kube-config:
image_pull_policy: Always
ovs_memory_limit: 1Gi
registry:
image_prefix: quay.io/noiro
Sample agent-config File
apiVersion: v1alpha1
kind: AgentConfig
metadata:
name: ocpvmw11
rendezvousIP: 192.168.12.3
AdditionalNTPSources:
- time.cisco.com
hosts:
- hostname: ocpvmw11-master1
role: master
interfaces:
- name: ens192
macAddress: 00:50:56:97:2a:d6
networkConfig:
interfaces:
- name: ens192
mtu: 9000
ipv4:
enabled: false
ipv6:
enabled: false
- name: node
type: vlan
mtu: 9000
state: up
vlan:
base-iface: ens192
id: 131
ipv4:
enabled: true
address:
- ip: 192.168.12.3
prefix-length: 24
dhcp: false
ipv6:
enabled: false
- name: infra
type: vlan
mtu: 9000
state: up
vlan:
base-iface: ens192
id: 3301
ipv4:
enabled: true
dhcp: true
ipv6:
enabled: false
dns-resolver:
config:
server:
- 192.168.12.2
routes:
config:
- destination: 0.0.0.0/0
next-hop-address: 192.168.12.1
next-hop-interface: node
- destination: 224.0.0.0/4
next-hop-interface: infra
- hostname: ocpvmw11-master2
role: master
interfaces:
- name: ens192
macAddress: 00:50:56:97:f6:65
networkConfig:
interfaces:
- name: ens192
mtu: 9000
ipv4:
enabled: false
ipv6:
enabled: false
- name: node
type: vlan
mtu: 9000
state: up
vlan:
base-iface: ens192
id: 131
ipv4:
enabled: true
address:
- ip: 192.168.12.4
prefix-length: 24
dhcp: false
ipv6:
enabled: false
- name: infra
type: vlan
mtu: 9000
state: up
vlan:
base-iface: ens192
id: 3301
ipv4:
enabled: true
dhcp: true
ipv6:
enabled: false
dns-resolver:
config:
server:
- 192.168.12.2
routes:
config:
- destination: 0.0.0.0/0
next-hop-address: 192.168.12.1
next-hop-interface: node
- destination: 224.0.0.0/4
next-hop-interface: infra
- hostname: ocpvmw11-master3
role: master
interfaces:
- name: ens192
macAddress: 00:50:56:97:07:42
networkConfig:
interfaces:
- name: ens192
mtu: 9000
ipv4:
enabled: false
ipv6:
enabled: false
- name: node
type: vlan
mtu: 9000
state: up
vlan:
base-iface: ens192
id: 131
ipv4:
enabled: true
address:
- ip: 192.168.12.5
prefix-length: 24
dhcp: false
ipv6:
enabled: false
- name: infra
type: vlan
mtu: 9000
state: up
vlan:
base-iface: ens192
id: 3301
ipv4:
enabled: true
dhcp: true
ipv6:
enabled: false
dns-resolver:
config:
server:
- 192.168.12.2
routes:
config:
- destination: 0.0.0.0/0
next-hop-address: 192.168.12.1
next-hop-interface: node
- destination: 224.0.0.0/4
next-hop-interface: infra
- hostname: ocpvmw11-worker1
role: worker
interfaces:
- name: ens192
macAddress: 00:50:56:97:b5:07
networkConfig:
interfaces:
- name: ens192
mtu: 9000
ipv4:
enabled: false
ipv6:
enabled: false
- name: node
type: vlan
mtu: 9000
state: up
vlan:
base-iface: ens192
id: 131
ipv4:
enabled: true
address:
- ip: 192.168.12.6
prefix-length: 24
dhcp: false
ipv6:
enabled: false
- name: infra
type: vlan
mtu: 9000
state: up
vlan:
base-iface: ens192
id: 3301
ipv4:
enabled: true
dhcp: true
ipv6:
enabled: false
dns-resolver:
config:
server:
- 192.168.12.2
routes:
config:
- destination: 0.0.0.0/0
next-hop-address: 192.168.12.1
next-hop-interface: node
- destination: 224.0.0.0/4
next-hop-interface: infra
- hostname: ocpvmw11-worker2
role: worker
interfaces:
- name: ens192
macAddress: 00:50:56:97:44:9b
networkConfig:
interfaces:
- name: ens192
mtu: 9000
ipv4:
enabled: false
ipv6:
enabled: false
- name: node
type: vlan
mtu: 9000
state: up
vlan:
base-iface: ens192
id: 131
ipv4:
enabled: true
address:
- ip: 192.168.12.7
prefix-length: 24
dhcp: false
ipv6:
enabled: false
- name: infra
type: vlan
mtu: 9000
state: up
vlan:
base-iface: ens192
id: 3301
ipv4:
enabled: true
dhcp: true
ipv6:
enabled: false
dns-resolver:
config:
server:
- 192.168.12.2
routes:
config:
- destination: 0.0.0.0/0
next-hop-address: 192.168.12.1
next-hop-interface: node
- destination: 224.0.0.0/4
next-hop-interface: infra
Sample install-config File
apiVersion: v1
baseDomain: ocplab.local
proxy:
httpsProxy: <http-proxy>
httpProxy: <https-proxy>
noProxy: <no-proxy>
compute:
- name: worker
replicas: 2
controlPlane:
name: master
replicas: 3
metadata:
name: ocpvmw11
networking:
machineNetwork:
- cidr: 192.168.12.0/24
clusterNetwork:
- cidr: 10.2.0.0/16
hostPrefix: 23
networkType: CiscoACI
serviceNetwork:
- 172.30.0.0/16
platform:
vsphere:
failureDomains:
- topology:
datacenter: k8s-scale
datastore: "/k8s-scale/datastore/k8s-scale-ds-esxi-3-raid5"
vcenters:
- datacenters:
- k8s-scale
password: xxx
port: 443
server: myvsphere.local.lab
user: administrator@vsphere.local
apiVIPs:
- 192.168.12.30
ingressVIPs:
- 192.168.12.29
fips: false
pullSecret: <RH-account-pull-secret>
sshKey: <host-ssh-key>
Post Install Configuration and Scaling
- As per https://docs.openshift.com/container-platform/4.14/post_installation_configuration/installing-vsphere-post-installation-configuration.html for installations using the Assisted Installer, you must update the connection settings. This is because the Assisted Installer adds default connection settings to the vSphere connection configuration wizard as placeholders during the installation
- Follow steps provided in the link: https://access.redhat.com/solutions/6677901 to modify the platform configuration which will provide cluster access to the vcenter.
- After successful completion of above step, cluster is ready to be scaled via machineset.
- Follow steps to create machineset as mentioned in the link: https://docs.openshift.com/container-platform/4.14/machine_management/creating_machinesets/creating-machineset-vsphere.html to scale the cluster.
Decommissioning OpenShift
Use this procedure to decommission OpenShift and remove the ACI-provisioned configuration from ACI.
Note Starting with Cisco APIC release 6.1, VMM domains for OpenShift cannot be removed from the APIC GUI. It is only possible using REST API, therefore, it is convenient to use the acc-provision tool to remove the VMM domain, and other related objects used by the decommissioned OpenShift cluster. Ensure you have the acc-input-config.yaml file and certificates used by the acc-provision tool to access APIC
Before you begin
In case of decommissioning or removing Openshift cluster, ACI configuration provisioned for that cluster should be removed from ACI. The acc-provision tool can be used to remove that configuration.
Procedure
Use the following command from the machine and folder which was used to provision the ACI infrastructure, to delete the pre-provisioned configurations and the VMM domain.
acc-provision -d -f openshift-4.14-agent-based-esx -c acc-input-file -u user -p password
Example:
acc-provision -d -f openshift-4.14-agent-based-esx -c acc-input-config.yaml -u admin -p password
Known Caveats
-
Installation hinders due to node Taints - https://access.redhat.com/support/cases/#/case/03682671
-
Storage Cluster Operator Degraded – Solution in progress - https://access.redhat.com/solutions/5926951
-
Assisted installer cluster installation fails with IP collision validation, due to a Porxy ARP request https://issues.redhat.com/browse/OCPBUGS-43352
Resolution
- Start the installation as usual
-
Get the Cluster ID:
curl -s http://rendezvousIP:8090/api/assisted-install/v2/clusters/ | jq ".[0].api_vips[0].cluster_id" - Disable Validations
curl rendezvousIP:8090/api/assisted-install/v2/clusters/<cluster-id>/ignored-validations -X 'PUT' -H 'accept: application/json' -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d '{ "cluster-validation-ids": "[\"all\"]", "host-validation-ids": "[\"all\"]" }' - If you observe the message below after running the previous step, wait until the installation reaches the stage where this error starts appearing
{"code":"400","href":"","id":400,"kind":"Error","reason":"Cluster 11467e69-dbad-4c70-a62c-ae2b83ba47e5 is in installing state, cluster can be updated only in one of [insufficient ready pending-for-input adding-hosts]"}